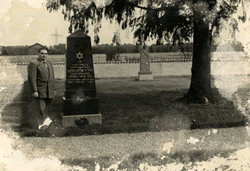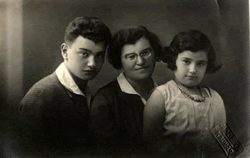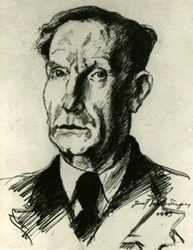#elkes-1:
Hans Malbin next to
the memorial to his brother-in-law Dr. Elkhanan Elkes, which he helped erect in the Jewish cemetery of Landsberg.
#elkes-2:
Miriam nee Malbin with her children Sarah and Joel Elkes. Kovno 1930.
#elkes-3:
Dr. Zvi Hirsh Elkes
(brother of Elkhanan Elkes) works in his physician's lab in prewar Koenigsberg.
#elkes-4:
Sara Elkes
#elkes-5
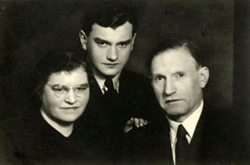
From left to right are Miriam nee Malbin, son Joel Elkes and Dr. Elkhanan Elkes.
#elkes-6:
Elhanan Elkes
Dr Elchanan Elkes was a doctor, a leading Zionist , and appointed the Chairman of the Jewish Council in Kovno on 5 August 1941. One of the three lawyers who helped Dr Elkes in his work recalled, " Never in the Kovno Ghetto was a Jew handed over by the Gestapo". Such was the reputation of Dr Elkes who was also to give active help to Jews in the ghetto who wished to train in the use of arms, to escape to the partisans, and to provide the partisans with equipment.
The Holocaust - Martin Gilbert, page 181
works in his lab in prewar Koenigsberg.
Biography:
Dr. Elkhanan Elkes (1879-1944) was a Jewish physician who, during the German occupation of Lithuania, assumed the leadership of the Jewish community in the Kovno ghetto. Born in Kalvarija, Lithuania, Elkes received his medical degree in 1903 in neurology and internal medicine. In 1912 he married Miriam Malbin. They had two children: Joel and Sarah. After serving as a physician in the Russian army, he opened a private practice and eventually became one of Kovno's leading physicians. In 1923 he was apppointed head of the department of internal medicine at the Bikur Holim hospital in Kovno. His numerous private patients included the Lithuanian prime minister, the German ambassador, and other members of the diplomatic community. In August 1941 the SS ordered Kovno's leading Jewish citizens to select a leader to head the new Jewish Council. No one wanted to assume this role. Finally the community prevailed upon Elkes, citing his connections and moral integrity. He remained in this position for all three years of the ghetto's existence. Despite his own failing health, he provided moral leadership, helped the ghetto's medical community, and provided tacit support to the underground. Much of the day to day running of the ghetto was entrusted to his deputy, Leib Garfunkel, an attorney and former Jewish delegate to the Lithuanian parliament. Elkes acted principally as an intercessor with the German authorities to ameliorate the severity of their orders. In one famous anecdote, shortly before the ghetto's liquidation, Elkes made a personal appeal to SS Captain Wilhelm Goecke. Elkes promised to write Goecke a personal testimonial if he spared the ghetto; Goecke refused. Elkes was deported to Dachau in July 1944. There, he continued to offer medical care to fellow Jews until he succumbed to starvation brought on by a hunger strike. He died on October 17, 1944 at the age of 65. Due to his stature, he was allowed a public burial in a marked grave. Elkes was survived by his wife Miriam, who had been deported to Stutthof, and his two children Sarah and Joel, who were studying in England during the war.
ELKES, ELHANAN (1879–1944), chairman of Kovno (Kaunas) Aeltestenrat (Council of Elders under the Nazis). Elkes was born in Kalvarija (Lithuania). He received both a traditional Jewish and a private secular education. Elkes studied medicine in Koenigsberg, Germany, was a village doctor in Belorussia, and then served as a physician in the Russian army during World War I before coming to Kovno, where he was director of internal medicine at Bikkur Holim. A respected physician, he treated prominent non-Jews as well as Jews and thus had excellent contacts, which he used when the Soviet Union occupied Kovno to assist in the emigration of Polish Jews stranded in Lithuania. Although an ardent Zionist from youth, he was not active in Jewish public life until the German occupation (June 1941), when he was unanimously elected chairman of the Kaunas Aeltestenrat, a position he accepted with great reluctance. Thus, he derived the legitimacy of his administration from the Jewish community and not from the Germans, who routinely appointed the Jewish leadership. Despite his failing health, Elkes guided the council for more than three years, during which time he took upon himself fateful decisions involving the future of the community while actively furthering the local resistance movement. He was a man of unquestioned integrity, who conducted the affairs of the Judenrat with equity and fairness, in marked contrast to other ghettos where corruption and the enticements of power – however limited and derivative from the German master – were rampant. Also in contrast with other Judenrat chairs, Elkes cooperated with the resistance. In Kovno the Jewish police directly assisted the partisans. In 1942, word of the fate of Polish Jews reached Kovno through Irena Adamowicz, a non-Jewish courier for the underground. From then on the members of the Jewish Council understood they would lead the battle for survival even without knowing if their efforts could postpone or prevent the day of destruction. Despite the Judenrat's best efforts, only 2,000 Jews – 8 percent of the ghetto's original population – survived, a rate little different from that of other ghettos whose internal governance was more corrupt and less benignly guided.
By his personality and dignity of bearing Elkes represents an outstanding example in the history of imposed Jewish "self-government." He wrote of his fate in a letter to his children, who were safe in England (written on October 19, 1943).
I am writing these lines, my dear children, in the vale of tears of Vilijampole, Kovno Ghetto, where we have been for over two years. We have now heard that in a few days our fate is to be sealed. The Ghetto is to be crushed and torn asunder. Whether we are all to perish, or whether a few of us are to survive, is in God's hands. We fear that only those capable of slave labor will live; the rest, probably, are sentenced to death.
We are left, a few out of many. Out of 35,000 Jews of Kovno, approximately 17,000 remain; out of a quarter of a million Jews in Lithuania … only 25,000 live … The rest were put to death in terrible ways by the followers of the greatest Haman of all times and generations …
We are trying to steer our battered ship in furious seas, when waves of decrees and decisions threaten to drown it every day. Through my influence I succeeded, at times, in easing the verdict and scattering some of the dark clouds that hung over our heads. I bore my duties with head high and an upright countenance. Never did I ask for pity; never did I doubt our rights. I argued our case with total confidence in the justice of our demands.
The Germans killed, slaughtered and murdered us in complete equanimity. I was there with them. I saw them when they sent thousands of people – men, women, children, infants – to their death, while enjoying their breakfast, and while mocking our martyrs. I saw them coming back from their murderous missions – dirty, stained from head to foot with the blood of our dear ones. There they sat at their table – eating and drinking, listening to light music. They are professional executioners.
I am writing this in an hour when many desperate souls –widows and orphans, threadbare and hungry – are camping on my doorstep, imploring us for help. There is a desert inside me. My soul is scorched. I am naked and empty. There are no words in my mouth.
Following the liquidation of the ghetto, he was deported to Lansberg, where he served as a physician before succumbing to illness on October 17, 1944.
Sources:L. Garfunkel, Kovnah ha-Yehudit be-?urbanah (1959); A. Turai, in: Heikhal she-Shaka, ed. by I. Yablokowski (1962), 235–49; Hidden History of the Kovno Ghetto, A Project of the United States Holocaust Memorial Council (1997); W.W. Mishell, Kaddish from Kovno: Life and Death in a Lithuanian Ghetto 1941 – 1945 (1988); A. Tory, Surviving the Holocaust: The Kovno Ghetto Diary (1990); J. Elkes, Values, Beliefs and Survival, Dr. Elchanan Elkes and the Kovno Ghetto: A Memoir (1997).
[Michael Berenbaum (2nd ed.)]
Encyclopaedia Judaica
Dr. Elkhanan Elkes (Elkis)
Birth:
1879
Kalvarija municipality, Mariampole Region, Lithuania
Death:
October 17, 1944 (65)
KZ-Dachau, Dachau, Oberbayern, Bavaria, Germany (Murderd by the NAZIS)
Immediate Family:
Son of Ysrael Meir Elkis, Rabbi and Sara Elkis
Husband of Miriam Elkis
Father of Dr. Joel Elkes Elkis and Sara Elkes
Brother of Julius Elkes; Dr Hirsch Elkes; Hannah Elkes and Arieh Elkes
#elkes-7:
Julius Elkes (brother of Elkhanan Elkes)
#elkes-8:
Dr. Hirsch (Tzvi) Elkes (brother of Elkhanan Elkes)
https://collections.ushmm.org/search/catalog/pa1175752
works in his lab in prewar Koenigsberg.